Wild Predators: A fun and informational look at predators

What is a predator?
Predators are animals that hunt and eat other animals. Weasels, hawks, wolves, mountain lions, and grizzly bears are all predators. Predators are carnivores, which means they eat meat. Predators come in many sizes and shapes. They can be as tiny as a bug or as large as a whale.
What does a ladybug eat? They eat other insects! Even the red breasted robin that signals the coming of spring is a predator.
Even though predators eat other animals to survive, they are not bad. They are just part of the earth’s ecosystem, like you and me, trying to make a living.
A simple food chain
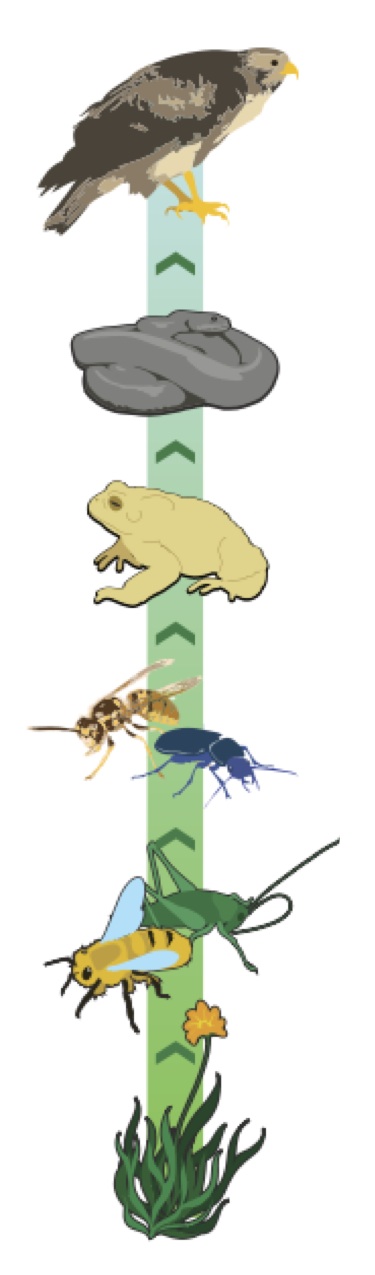
The role of predators
Predators are part of a food chain, the process of passing energy from one organism to another.
Plants are the first link in a food chain. They use nutrients from the soil and energy from the sun to make food.
- Plant eaters, called herbivores, are next in the chain. They use the energy from the plants they eat to help them grow and survive.
- Predators like birds, mice and foxes are next in line, eating the herbivores to survive.
- The final link in the food chain is the apex predator, the organism at the top of the food chain. In this example the apex predator is a hawk. When the hawk dies, it’s body decomposes and provides nutrients for plants to grow and the cycle
Most natural communities have several food chains that interconnect. This is called a food web. The relationship between predators and prey is often described as the balance of nature.
Can a predator also be prey?
Yes. In many cases animals that eat other animals will also become dinner for bigger and faster predators. In the food chain shown here, the honey bee may fall prey to a hornet, which in turn could be eaten by a toad. The toad could become a meal for the snake, which could later be eaten by the hawk.
As you can see, a food chain can become very complex. That is why having a lot of different organisms in an ecosystem is important. this large variety is called biodiversity.
Because predators survive by eating other animals, they greatly affect the food web. By keeping populations in check predators reduce the negative impacts that overpopulation of other animals can have on an ecosystem.
When predators eat deer they limits the affect deer have on plants. This allows more trees, shrubs, bushes, and grasses to grow, which provides additional habitat for other species.
This is how predators help to preserve biodiversity. Healthy natural systems provide us with clean water, healthy plants, natural pest control, fertile soil, disease control, and many other natural benefits.

What would happen without predators?
Lets take a look at just one prey animal, the mouse.
Without predators a single mouse mother could produce as many as 82,000 babies in a year.
Most mice live about two years where there are no predators. Over a two year life span a single mouse mother could produce 681,322,104 babies.
In two years a mouse, along with it's babies and their babies, could produce nearly 700 million offspring. They would weigh as much as three thousand african elephants. That many mice would eat more than a million and a half pounds of food a day.
Predators come in all different shapes and sizes
VERTEBRATE PREDATORS
| INVERTEBRATE PREDATORS
| PLANT PREDATORS
|
|---|---|---|
Wolf
| Spider
| Venus Flytrap
|
Hawk
| Lady Bug
| Picture Plant
|
Snake
| Praying Mantis
| Sundew
|
Bass
| Ant Lion
| Bladderwort
|
Different Types of Predators
VERTEBRATES
Animals with an internal skeleton made of bone are called vertebrates. Vertebrates include mammals, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and fish. Even though these animals make up a very small portion of the total biomass they are very visible and perhaps the best known of the predators.
INVERTEBRATES
Animals who do not have back bones are called invertebrates. They are cold-blooded, meaning their body temperature depends on the temperature of the environment around them. Some invertebrates include amoebas, corals, worms, insects, arachnids, crustaceans, and mollusks. There are more species of invertebrates than any other living group on earth.

PLANTS
There are even plants that are "meat-eaters. Many of these plants live in areas with little or no nutrients in the soil. They need to get their energy from another source. In this case, they eat small animals and insects to provide what they need to survive and grow.
How do predators catch their prey?
Hunting Strategies
The way a predator hunts, catches and kills food is determined by many factors such as the adaptations of the predator and the prey, and the type of habitat they live in.
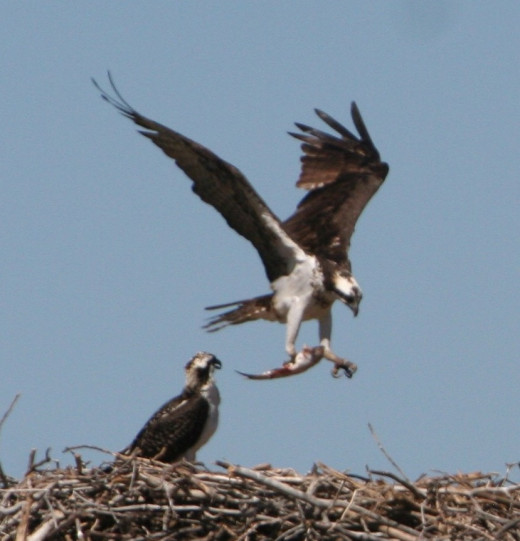

The Chase
Osprey are among the many predators that catch their prey by chasing it. Chasing prey takes a lot of time and effort. Many of the chases don't result in a capture. To survive, predators that chase their prey must pursue animals that are worth the effort. Some animals hunt prey that is big enough to provide several days of eating. Unless smaller prey is very abundant and easy to catch most predators won't waste the effort in pursuing them.
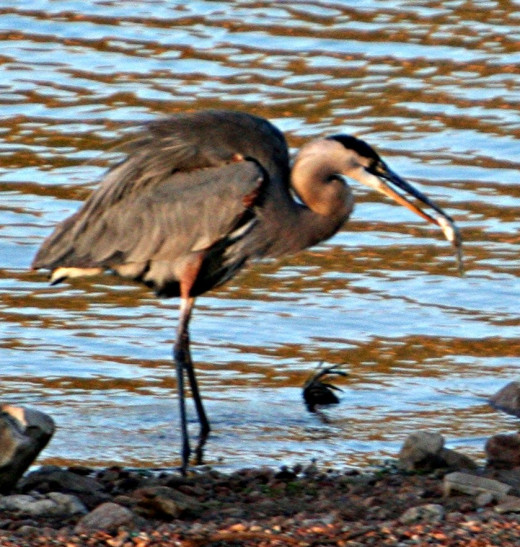

The Stalk
Herons use a different technique, they stalk their prey. By standing motionless or slowly wading in shallow water herons use stealth as they search for food. When a heron sees its prey it will use its coiled neck and long sharp beak to catch unsuspecting fish or crustaceans. This technique doesn't expend much energy, but does take a lot of time. A predator that stalks its prey can focus on smaller animals to give it enough to eat.
The Ambush
Many reptiles are ambush predators. Because this method requires minimal effort it fits in well with the cold blooded reptiles. Because of their reduced metabolism many reptiles can go for days without eating. Because they need to be closely approached by their prey, most ambush predators are smaller and well camouflaged with very fast reflexes.


Teamwork
Some animals hunt as teams. Wolves, lions, hyenas and killer whales are good examples. By hunting as a group these animals are able to hunt larger and faster prey. Army ants are another example of a predator that hunts as a group.
Some predators have become skilled at using more than one hunting method. For example, The cougar will use a combination of the ambush, stalk and chase. They will wait patently in an area frequented by their prey, stalk to within striking distance and then launch into a short but fast chase to catch their dinner.
Some predators are also scavengers
Many predators are not too proud to pass up a free meal. If they can find or steal a dead animal they will take advantage of an easy opportunity to fill their bellies. Click on the video to see a young grizzly eating the very last morsels of meat on a carcass that was left by a bigger grizzly.
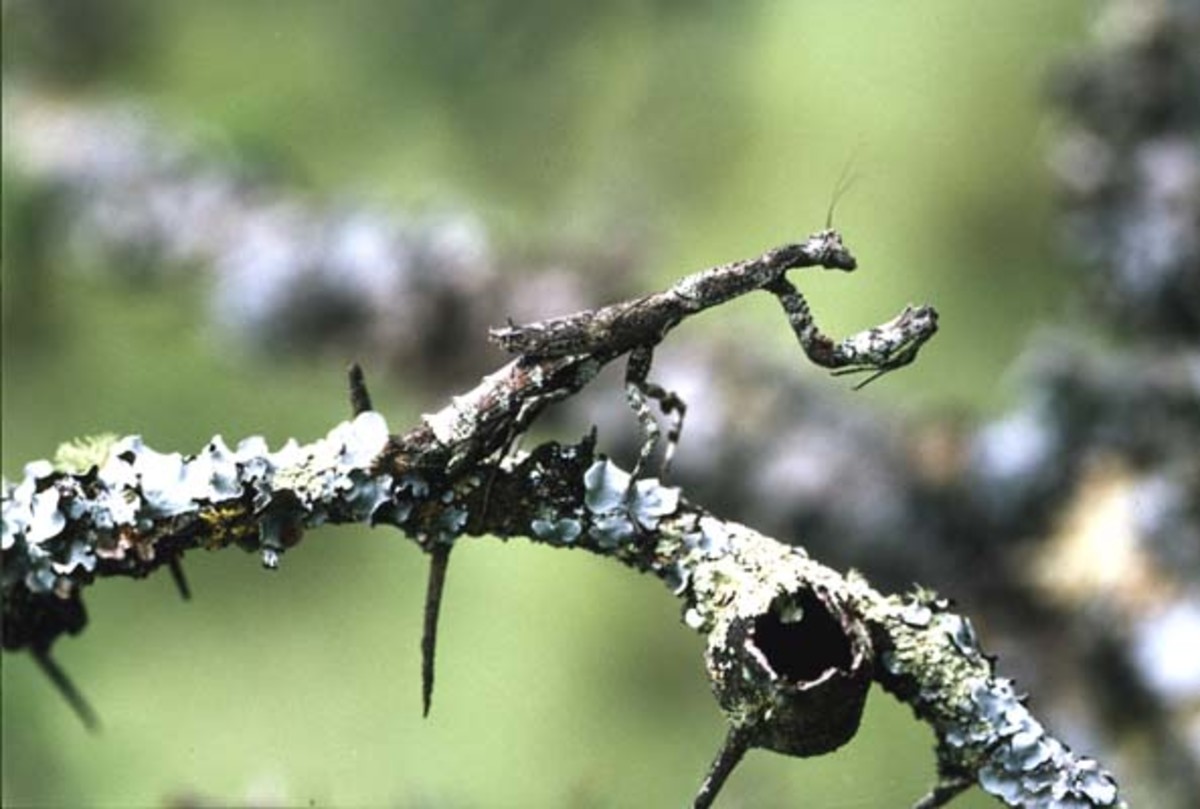
Natural Camouflage
Wild animals use three different types of camouflage. Both predators and prey animals will take advantage of these characteristics. Predators will use them to get close to food and prey animals use it to avoid detection and thereby avoid becoming a meal.

1. One camouflage method is when an animal's color is similar to its surroundings. For example, desert animals are usually different shade of brown. Animals that live in jungles are more often greenish in color.

2. Another type of camouflage is called counter shading. A counter shaded animal is darkest on the top of its body and lightest on the bottom. From a distance these animals seem to turn into one color and look flat.
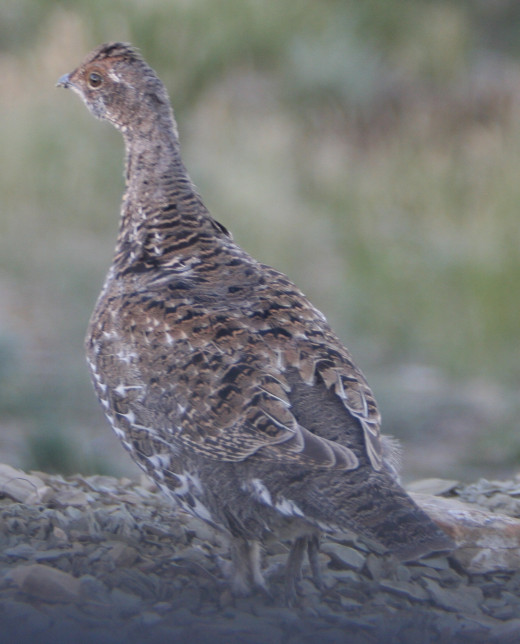

3. The third type of camouflage is disruptive coloration. Zebras, tigers and rattlesnakes are all good examples of animals that use this technique. By breaking up their body outline with irregular spots or stripes of different colors or shades these animals make it harder to identify they as what they are.
Some animals change color with the season. This helps them to blend in with their surroundings when their surroundings change.
Making sense of senses
Different predators will make use of different senses to find their prey. The three main predatory senses are sight, smell and hearing.
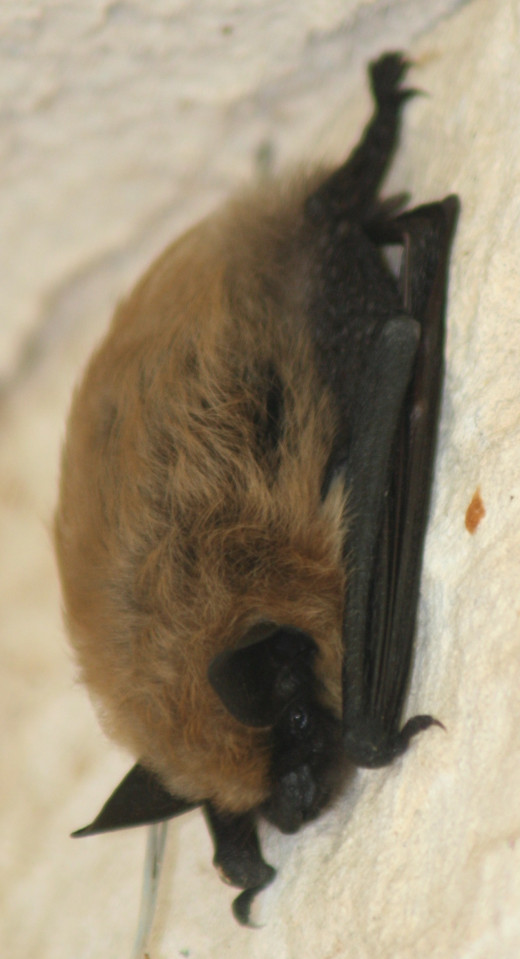

Hearing
Many predators have an excellent sense of hearing, but perhaps the ultimate hearing award should go to the bat. These amazing predators use echo location to navigate at night and locate insects to eat. A single bat can catch as many as a thousand insects an hour.
Some groups of Mexican free-tailed bats contain millions of bats. In those colonies it is estimated that 250 tons of insects can be consumed every night. That's as heavy as 83 African elephants.
Smell
Animals that have good senses of smell will usually have a long nose. Members of the dog family like coyotes and wolves have great sniffers, but bears can smell 700 times better than a bloodhound. Scientists believe that polar bears can smell seals from as far away as 20 miles.

Sight
Raptors like eagles and owls are famous for their eyesight. Members of the cat family are also blessed with great vision. Their eyes are large in relation to the rest of their skill and are located on the front of their face. This gives them better binocular vision and makes them better at judging distance. This is critical in allowing them to gauge how far away a prey animal is so their pounce will be on target.







